The Kano model is a theory of product development and customer satisfaction developed in the 1980s by Professor Noriaki Kano.
Customer satisfaction is a measure of how products and services supplied by a company meet or surpass customer expectation.
It is defined as "the number of customers, or percentage of total customers, whose reported experience with a firm, its products, or its services (ratings) exceeds specified satisfaction goals.”
Customer satisfaction is a measure of how products and services supplied by a company meet or surpass customer expectation.
It is defined as "the number of customers, or percentage of total customers, whose reported experience with a firm, its products, or its services (ratings) exceeds specified satisfaction goals.”
Customer satisfaction and User Experience
Customer satisfaction comes from a Product or service.
User Experience comes from overall journey related to a product/service, like buying product, using product, maintenance services etc.
Kano’s model in detail
The Kano model is a theory of product development and customer satisfaction which classifies customer preferences into five categories.
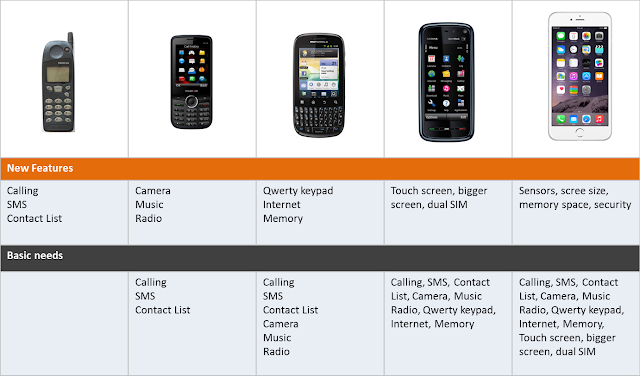
1. Must-be Quality (Basic needs, Dissatisfies)
These attributes are taken for granted when fulfilled but result in dissatisfaction when not fulfilled.2. One-dimensional Quality (Performance, satisfiers)
These attributes result in satisfaction when fulfilled and dissatisfaction when not fulfilled.3. Attractive Quality (Delighters or Excitement Needs)
These attributes provide satisfaction when achieved fully, but do not cause dissatisfaction when not fulfilled.4. Indifferent Quality
These attributes refer to aspects that are neither good nor bad, and they do not result in either customer satisfaction or customer dissatisfaction.Kano Model Diagram
Kano diagram is represented below with all types of needs in single graph.














%20in%20India.png)