Updated on 20 Nov 2025, Published on 18 Feb 2024
User Research uncovers the needs, behaviors, and attitudes of a product's users. It allows designers to look at the product through the lens of their users, helping to create a website or app that satisfies their unique needs.
Good user research guides digital designs to be effective and relevant. It bases design choices on real data, not just guesses. In this article, we’ll explore what user research is, its types, and how to conduct it.
What is User Research?
User Research is a process that involves various research methodologies that aim to understand users' needs, expectations, and behaviors while using a product or a service.
User research can involve a range of activities, including surveys, interviews, usability testing, observation, and analysis of how users interact with a product or service. The goal is to gather insights that inform the design process, making products more usable, accessible, and enjoyable for users.
User Research VS User Testing
While user research fundamentally expresses an understanding of the user's world, user testing examines how well a specific product performs in that world.
User research encompasses a broad spectrum of activities aimed at gathering insights about the user's behaviors, needs, and motivations before a product is fully designed. It helps in shaping the initial concept and development of a product, ensuring it meets the users' expectations from the ground up.
User testing, on the other hand, is often conducted later in the development process and focuses on evaluating the usability and overall experience of a product by observing real users interacting with it.
This direct feedback loop is crucial for identifying any usability issues or areas for improvement, allowing teams to make informed adjustments that enhance the product's effectiveness and user satisfaction.
Together, user research and user testing form a comprehensive approach to creating user-centered designs that truly resonate with the target audience.
Types of User Research
In this section, we will delve into the various types of user research. The type of research that's most appropriate depends largely on what we aim to know.
Qualitative VS Quantitative User Research
Qualitative research provides insights into the user's thoughts, emotions, and preferences. It helps answer 'why' and 'how' questions about user behavior, offering extensive detail.
Qualitative research methods, often non-statistical, include interviews, observation, and usability studies. Conversely, quantitative research helps to uncover numerical data to statistically provide 'what', 'where', 'when', and 'who' answers.
Leveraging methods like surveys, A/B testing, and website analytics, it depicts broad patterns and trends, arming you with data on user actions at a grand scale.
Moderated VS Unmoderated User Research
Moderated user research involves direct interaction between the researcher and the participant.
This is typically done through interviews, focus groups, or usability testing, where the researcher has the opportunity to guide research, probe, clarify, and observe user responses.
On the other hand, unmoderated user research is more autonomous. It happens without a facilitator. The users undertake tasks independently, such as website testing or surveys. This provides undiluted feedback and user experience, all in a more timely and cost-effective manner.
Formative VS Summative User Research
Formative research focuses on uncovering issues during the development stage of a product, creating a platform for continuous changes and improvements. It primarily works as a preventive measure to determine usability glitches or user expectations beforehand.
Summative research, on the flip side, assesses an already built product/wireframe against certain predefined criteria or benchmarks, providing measurable results. As the name suggests, it sums up the strengths and weaknesses after the user interacts with the design, allowing for informed revisions in subsequent versions of the product.
In-person vs. Remote User Research
In-person user research involves face-to-face interactions with users, valuable for capturing body language and immediate responses.
This can be through interviews, focus groups, or direct observation. However, geographical and logistical restrictions could make this challenging at times. Remote user research overcomes these limitations, making use of technologies like video conferences and online surveys for data collection.
While it allows for wider reach and convenience, it may limit the depth of information obtained, especially nonverbal cues, which provide rich insights about user behavior.
Exploratory VS Descriptive User Research
Exploratory research aims at uncovering the unknown—at seeking out new information and ideas. It delves into users' attitudes, behaviors, needs, and motivations to broadly explain patterns and themes.
Descriptive research, however, is more structured, focusing on depicting users' actions and habits in specific detail and quantifiable measures.
This type of research embodies methods like surveys and longitudinal studies and illustrates an accurate snapshot of gently profiled issues and user trends without manipulating the study environment. Hence, both types offer substantial insights, serving different research stages and needs.
User Research Methods
In this section, let's delve into some of the most common user research methods.
Usability Testing
Usability testing is a method of evaluating the usability of your digital product (website, app etc.) by asking users to complete specific tasks and watching them do it. It gives deep insights into user behavior and helps to spot usability issues, areas of confusion and improvement.
Usability testing is usually performed online with the help of a usability testing tool but can sometimes take place in an in-lab environment.
Learn the basics of usability testing in this quick video:
https://youtu.be/PiyrpfCD2-E
A/B test
A/B testing is a comparative user research method where two different versions of the same design are presented to users. Observations about their responses, preferences, and difficulties with each design are duly noted.
For instance, two different homepage layouts of a website could be tested to determine which one gets more clicks or prolongs user time on the page.
This method is immensely powerful in making data-driven decisions, choosing the design option based on user feedback and not just vague assumptions.
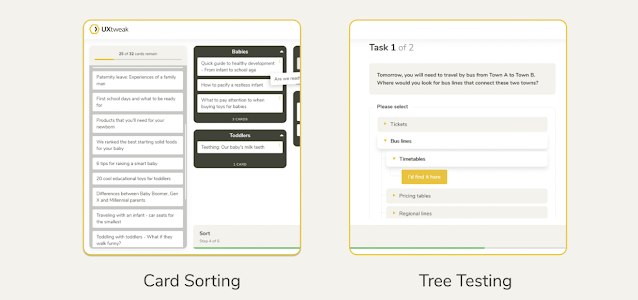
Card Sorting and Tree Testing
Card Sorting and Tree Testing are interactive methods used to understand how users think and categorize information.
In Card Sorting, participants group digital or physical 'cards' in ways that make sense to them. The results offer insights into how users perceive associations and categories, which can assist in designing a user-friendly navigation system.
On the other hand, Tree Testing evaluates the usability of information architecture without the influence of visual design or navigation tools. This helps identify accessibility challenges and informs improvements to the structure of content.
User Interviews
User interviews are a core method in user research, offering valuable in-depth insights directly from users themselves.
The process involves asking users a series of questions to gain a deep understanding of their experiences, observations, and opinions, shedding light on their behaviors and attitudes.
One of the strengths of this method is its versatility, as each interview can be customized to the specific user and research objectives. However, it's important to note that skilled facilitators are needed to extract meaningful information because user responses are often influenced by the questions asked and how they are framed. Additionally, real-time clarification of ambiguous answers is possible during interviews, enhancing the quality of the data gathered.
User Research Process
Let's investigate the main stages involved in conducting fruitful user research.
Step 1: Study Goals
The initial stage revolves around defining the purpose of the research.
What do you expect to learn from it?
What specific problems do you seek to solve?
Are there particular areas of your product you want to focus on?
Who is your target user, and what do you know about their habits?
What research methods are most appropriate to achieve these objectives?
Understanding these will shape the direction of your study, where it will take place, and determine who your participants will be. This step ensures you establish clear, specific, and measurable goals, making the overall process more targeted and effective.
Step 2: Choosing the Right User Research Method
Next, you should identify which research method will best aid in achieving your outlined objectives.
Different methods yield varying data, each suitable for distinct research questions. Hence, the selection must align with your goals and available resources.
Consider factors such as target demographic, time constraints, your team's expertise, and the type of information sought, among other variables.
It could be one-on-one interviews for detailed responses, surveys for broader reach, usability testing for functionalities check, A/B testing for comparison, or a combination of two or more methods for more in-depth insights.
Step 3: Creating the Study
Now's the time to create your study's design.
Create a User Research Plan: Document the scope of your research, what will be studied, when, where, and how. Outline the methods, tasks, and sampling details to ease execution.
Develop Instruments: Design questionnaires, layout prototypes, create facilitator guides, etc., as required for your chosen method.
Implement Mock Test: A dry run of your detailed plan can uncover imperfections and improve your research's effectiveness by modifying necessary elements.
Make Participant Arrangements: Identify the target audience of your research, reach out to respondents, confirm participation, and communicate study details.
Whether you're conducting research for a completely new product or an existing one, maintaining clarity, organization, and meticulous attention to detail is crucial for gathering valuable qualitative and quantitative data. These principles help ensure that the research process is well-structured and the data collected is reliable and insightful.
Step 4: Choosing the Right User Research Tool
Once you have established the foundation of your study design, the next essential step is choosing the appropriate tool to facilitate your research. The selection of the tool largely depends on the specific research method you have chosen.
There are all-in-one research tools like UXtweak that offer all the methods you need like surveys, usability tests, heatmaps, card sorting and tree testing in one place.
Or you can choose to go for specialized tools like SurveyMonkey for surveys, CrazyEgg for session recordings, etc.
User Research Through Product Development
In this section, we mention the stages of the product development lifecycle and why user research should be conducted during each stage.
1. Identifying User Needs
This stage is the foundation of product development and the stepping stone for all the subsequent processes. Here, user research comes into play to identify user needs and expectations. Surveys, interviews, and observational studies can provide a direct glimpse into the user's world.
2. Idea Conceptualisation
In this stage, all the gleaned user insights are utilized to shape an initial idea into something more concrete. It's about drafting a usable and attractive product that users want. Here, the spotlight goes to user personas and prototyping. Testing prototypes with users gives further insights into product design improvement.
3. Prototype Development
When the set blueprint transitions into a tangible form, a product prototype comes into play.
At this point, user testing becomes paramount. Consider using a Prototype Testing Tool by UXtweak to test how users interact with your prototypes and where they encounter issues.
This stage can help to spot and correct design flaws early, improve the user interface based on actual user feedback, and eventually save time and resources in the final stages of production.
4. Market Testing Stage
After fine-tuning the prototype to near perfection through user testing, the product is now ready to undergo mock-release or market testing. This phase involves launching the product in controlled or test markets to gather feedback from a real-world audience.
Research methods like usability testing, A/B testing or direct customer feedback help you nullify errors and further polish the product. The insight gained equips you better for a successful official product launch.
Best User Research Tools
UXtweak
UXtweak is an all-in-one UX research tool that has grown a lot. It has all of the capabilities to take advantage of almost any research method to cover all your research needs.
The comprehensive set of remote user research tools to collect real user insights, and advanced analytics options to recruit research participants, combined with a great UI, that is easy to understand even for a complete beginner – UXtweak has everything you need for your research projects and more.
Features:
Website Usability Testing Tool
Session Recording with Website Heatmaps (Click, Scroll, Move, Tap)
Mobile App Usability Testing
Prototype Testing (Figma, Invision, Axure)
Card Sorting Tool
Preference Tests
5 Second Test
First Click Test
Online surveys
Competitive Usability Testing
Pricing:
UXtweak offers a free starting plan. You may also choose between Plus plan aimed at solo researchers for $49 per month (annual billing) or a Business plan with up to 11 seats. If that is not enough you can get your custom Enterprise plan tailored to your specific requirements.
Crazyegg
Crazyegg serves as another valuable addition to your UX research toolkit, brimming with features like heat mapping, A/B testing, and visual analytics. Its strengths lie in capturing and comparing design variations, rigorously bringing user behavior into focus.
This enables you with a clearer understanding of your site's user interaction and gives you the strategic keys to unlock improved website optimization. Furthermore, its insightful analytic views, coupled with snapshots and elements analytics, arm you with a targeted approach to navigate your customer's needs.
Features:
Snapshot reporting
Heatmaps and scroll maps
Session recordings
Demo dashboard
Pricing:
Its basic plan starts at $29/month, billed annually, and goes up to $249/month, depending on the number of page views and recording you need. An enterprise plan is available.
UserTesting
UserTesting lends a different angle by specializing in real-time user feedback. This remote user testing tool gives you insight into how people interact with your product straight from the user's perspective.
Features such as Live Conversation, Views & Annotations, and the ability to run Subscriptions as well as Research Tests cater to a diverse set of needs.
The richness of qualitative Deficiency Analysis, combined with the inclusion of analytics, helps uncover points of friction swiftly and accurately.
Features:
Website testing
Mobile application testing
Prototype testing
Card sort & Tree test
Preference test
5 second test
Survey tool
1:1 interviews with testers
Video recording
Pricing
Upon request, starting at $30,000K/year. Annual subscription only.
Hotjar
Hotjar is another extremely useful tool in any UX researcher's toolbox. It provides heat mapping, session recordings, and other useful features to deliver insights into what's working and what's not within your website or application. Its comprehensive analytics help to highlight areas where users may be struggling, while survey tools gather direct feedback for deeper analysis.
Features:
Heatmaps
Visitor recordings
Conversion funnels
Feedback polls
Incoming Feedback
Pricing:
Free plan is available. The fee-based plans start from $32 and go up much higher, depending on your needs.
Wrapping Up
There you go—a brief overview of why and how to conduct user research throughout product development, accompanied by some of the best tools available.
Being user-centered is paramount in the current digital age. Ensuring that your product or service caters to its intended users can maximize ROIs and encourage positive brand experiences.
The right combination of detailed user research and effective tools can pave the way for a user-centered design process and eventual product. To summarize - listen to your users, learn from their insights, and leap into seamless product development.
FAQ
What is User Experience?
User Experience, often referred to as UX, is the overall feeling a user has while interacting with a product or service. It encompasses all aspects of a user's interaction with a product, from the effectiveness of site navigation to the emotional response provoked by the design.
UX is about making a product or service user-friendly, satisfying, and seamlessly functional. A well-established UX initiates satisfaction among users. This encourages them to return and continue using your product, choosing it over your competitors.
2) What is user research?
User research is a methodological approach utilized in the field of design to comprehend user behaviors, needs, and motivations through observation and feedback collection. This process ensures the designed product meets end user requirements effectively, making the user experience more enjoyable and beneficial. It eliminates guesswork and assumptions, leading instead to data-driven decisions. Multiple methods are often employed in its execution, such as user interviews, surveys, and A/B testing, each providing useful insights to better shape and refine a product or service.
3) How to conduct user research?
To carry out user research, start by defining your objectives to steer the entire process. Choose the most appropriate research method to track toward those objectives. Once that is done, shape your study by detailing your plan, developing necessary tools, conducting mock tests, and arranging participant logistics. Select the right tool as per your study design like SurveyMonkey for surveys or UXtweak for usability tests. Then perform research through each stage of your product development lifecycle, refining based on continual user feedback. User research is all about iteration!
4) What is an example of user research?
An example of user research could be online surveys for a new fitness application. You could ask potential users what functionality is most important to them in a fitness app, such as the ability to track different exercises, calorie intake, or heart rate. Collecting and interpreting these responses would help design the app in a user-centric way. Additionally, user testing or feedback on an initial design prototype would be another example where certain features or layouts are refined against user suggestions or difficulties.
DISCLOSURE: This article is published as part of a paid partnership with the author/company. The views and opinions expressed are those of the author/company.

.png)










%20in%20India.png)