Sunday, 5 December 2021
Thursday, 11 November 2021
10 Technical Skills for UX Designers
Remember when Elon Musk said, "any product that needs a manual is broken"? This quote pretty much summarizes which type of UX design skills you should master.
To put it simply, User Experience (UX) refers to any user's interaction with apps or websites. More than aesthetically pleasing, the point is to create a smooth and intuitive experience for the user. When the user needs a manual to understand how to purchase a shirt on a clothing app, then they will probably look for another shirt in a different app.
Table of Content
- Why Are UX Design Skills Important?
- 10 Technical Skills For UX Designers
- UX writing
- Research on User Persona
- Wireframing & Prototyping
- Mockup & Client Stream
- Information architecture
- Visual plan and plan programming
- Client examination and convenience testing
- Application development
- Data Engineering
- Agile
- Last Thoughts On UX Design
Why Are UX Design Skills Important?
UX design skills are important to satisfy the user's needs. The scope is to create a positive experience to build a loyal audience and increase a company's leads. In short, users have a good experience when they feel as if they have always been using that website or app.
Just think about it. People go on apps and websites to accomplish a certain action with the minimum effort. When completing a step becomes too complex, 90% of users stop using the app looking for alternatives. Pioneer in User Experience and Information Architecture Peter Morville isolates seven principles to create a great user experience: Useful, Usable, Findable, Credible, Desirable, Accessible, and Valuable.
The core idea behind these principles is that the aesthetic of the app or website is strictly related to its usability. In other words, an app is beautifully made when colors and features make the users' life as simple as possible.
Let's look at the 10 technical UX design skills anyone needs to create a smooth and interactive experience for users.
10 Technical Skills For UX Designers
1. UX writing
UX writing includes every visual feature on the interface. From headings, microcopies to buttons and menu bars, UX designers take care of everything. Based on users' feedback and responses, the writing process aims to improve the usability and readability of the interface. Each element is created to guide users from the beginning to the end, encouraging them to stay on the page and complete different actions.
2. User Persona
Without in-depth research on user personas, it's impossible to create a good UX design. User research happens at the beginning of the process to target UX writing features. This research includes creating buyer personas, identifying several elements such as demographics, motivations, behaviors, and habits. Further, UX designers analyze competitors to find alternative visual strategies to capture users' attention and empathize with the product.
3. Wireframing & Prototyping
To a considerable extent, a UX designer's research is based on User Feedback. At the beginning of the development process, wireframing (a blueprint of the product concept) and prototyping the app/website are crucial strategies to gather information. Combined with research on buyer personas, collecting (and interpreting) users' feedback is necessary to target and design visual features on the interface.
4. Mockup & Client Stream
Another important UX design skill is creating mockups and client streams. The first is a visual model of the page, like what clients can usually do with self-guided web design software, and the next one is a graph visualizing the customer journey. Strictly related to wireframes and prototypes, a UX design needs to understand the user's actions to adjust visual elements and graphics.
5. Information Architecture
When it comes to user experience, aesthetics connect with usability. Information architecture is the process of organizing content to show users the interface's functionalities. The scope is to overview the app/website options to adjust each on the user's journey.
6. Visual Plan
Together with UI designers, UX designers need a basic understanding of visual plan programming tools like Figma, Sketch, Photoshop, or Illustrator, to create the visual components. Visual planning also includes shading hypothesis, typography, format, symbols, and general plan hypothesis.
7. Client Examination and Convenience Testing
To create a focus-user interface, client examination and convenience tests are the last steps. Creating a model based on future customers' needs, you can guide clients through the app and show how the design encourages actions on the page. This stage is crucial to make your clients approve the model. So, it's important to include data from surveys and client streams to illustrate the visual components and flow of the interface.
Thursday, 9 April 2020
Getting closer to Multimodal Interaction
Image courtesy of Csanády Szilvia

Now comes the next great thing, living in sophisticated society, humans interact and communicate with other humans namely your parents, siblings, friends, colleagues & pets if they are not with family, whether it is for a want or a need like baby crying for milk or you are standing in grocery store with cart filled with stuff that needs to be billed. So, we perceive things from various senses governed by our brain what to do next. Standing in queue you cautiously think what to do next, who is in front of you, what is the space between you and the other person in queue, you see little space you slowly move forward so that you get closer to the billing counter.

Image courtesy of JERAMEY LENDE/SHUTTERSTOCK
Let’s just analyze this situation you look for the gap and push the cart slowly front or back depending on how you are placed, the angle, some obstacle, the rung along the side way, the partition that divides the counters. If your cart is heavy you push a bit hard, being cautious not to ram the person in front of you and even if you did push the person ahead of you, you apologize in advance or soon after you crash into them. You might also prepare yourself to pay which mostly consist of keeping your credit card in front pocket in advance, so you don’t waste your time, the cashier’s time and the person behind you. So, this is the level of interaction and thought goes in a small event of buying your groceries.
 Image courtesy of Jagoda Jankowska
Image courtesy of Jagoda Jankowska We could extend this to anything we do in the real world whether you are filling a form, watering a plant, cooking your favorite meal, tuning your guitar, driving car in an unknown area we collaborate with things which helps us to get our things done. It’s very common now a days to cook checking Google home hub or controlling your smart bulb or curtain or windows to open or close. Looking at these examples what is understood is we like to do more in less, you name it multitasking or smart automation the idea always is to make things easier, faster and simpler.
What is Multimodal Interaction or MMI?
Multimodal Interaction or Multimodal human-computer interaction refers to the “interaction with the virtual and physical environment through natural mode of communication”, here users are facilitated with multiple modes to interact with the system. This means users have 2 or more combined input modes to interact with this could be a combination of touch, gesture, gaze, speech, facial expression to provide simple, efficient, pleasant experience to user while they are performing their task.
How does Multimodal interaction work?
Multimodal interaction is similar to any other interaction, but the user has multiple option to interact with again this comes at its own price designing and developing. The user could use any of the available modes to interact at his convenience, the main idea of multimodal interaction is to allow user with multiple option depending on user’s convenience. Consider you are in middle of an activity and you want to multitask without stopping something completely but continue both the activity. Consider your playing a chord on your guitar and want to go to next sheet or you are thinking aloud and dictating the report that you want to type.
 Artwork by Author
Artwork by AuthorTable below shows the most commonly used Interaction and Perceiving modes acquiring knowledge about the state of the system and taking action. The below list is for general users and technology that are most commonly used, for special users with impairment, elderly users and technology specific devices the list would be specialized for the specific user, associated technology.
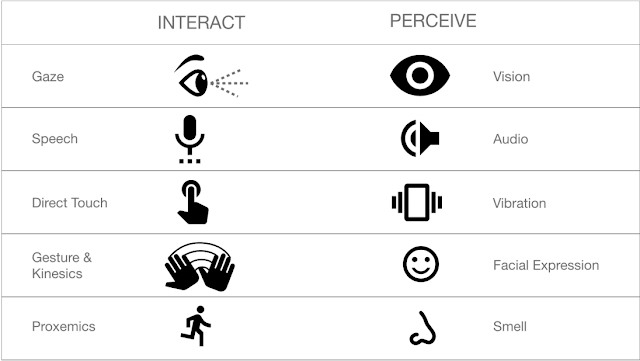
Table by Author
The main idea of multimodal interaction is to give more freedom and control to the user by provide more than one way to interact with the system as the idea of interaction constrained to one type is always not beneficial to users as we don’t know what the situation of user is at that very instant. You could be driving, cooking, running, walking, exercising, showering, with occupied hands, hearing to something, looking at something, travelling, where in you cannot stop the thing you are doing.

Artwork by Author
The above illustration shows the possible interaction that a User can have with the system based on available degrees of freedom for interaction, limitation of technology with the system and situation of the user using the device (system).
The different interactions available for user is not to over whelm but to help in successful task completion making it simple, efficient and pleasant to user as we are do not know the users context.
Do I really need multimodal interaction?
Before even questioning about do we really need multimodal interaction lets understand how we interact with different devices and applications depending on need and on daily basis. Most of the devices are designed for multimodal interaction be it a sophisticated computer, a smart tv and what not. Multimodal interaction is constantly evolving The below list gives an idea of available devices that most of the us interact with.
Stationary Connected Devices
• Devices - Desktop computers, Home appliances with display panels, embedded devices , smart home hubs
• Connectivity - Wired networks, wifi, paired devices
• Portability - Users are accustomed using these devices in the same location and setting on a habitual basis
• Interaction - Main interaction consist of an Screen or Monitor with input device namely mouse, keyboard, pen, remote, touch screen. Quasi-standardized methods of voice interaction between similar device genres (desktop computers vs. connected hubs like Google Home/Amazon Alexa vs. smart thermostats).
Phones
• Devices - Android, I-phones, Phablet, blackberry,
• Connectivity — Cellular networks, wifi, paired devices
• Portability – Used on the go, mostly not stationary. Environmental context has a substantial impact on voice interactivity
• Interaction - Users are accustomed to using voice interaction. Allows interaction through visual, auditory, and tactile feedback Interaction methods are fairly standardized across models.
Wearables
• Devices - watch, fitness band, smart shoes, ear pods
• Connectivity — Cellular networks, wifi, paired devices
• Portability - Used on the go, mostly not stationary
• Interaction - Users may be accustomed to using voice interaction, visual and tactile are more passive with no explicit user interaction
Non-Stationary Computing Devices (Non-Phones)
• Devices - Laptops, tablets, transponders, automobile infotainment systems,
• Connectivity — Wireless networks, wired networks (not common), wifi, paired devices
• Portability – fixed to limited mobility
• Primary input mode is typically not voice, has tactile, connected/integrated input devices
Based on interaction the devices normally seen are:
Screen-First devices
Devices that allow interaction from the GUI here the devices could be touch or devices which takes input including keyboard, mouse, pen, digital, analog buttons and embedded devices.
Voice Agents In Screen-First Devices
Devices that use primarily GUI and has voice actions as enhancement that adds up to the GUI., the user here interact with voice and the touchscreen.
Voice-Only Devices
These devices don’t have visual displays and users rely on audio for both input and output. This makes them limited to specific function and are aimed for specific task including some standard usage like knowing weather, reading mails, playing music, movies.
Voice-First Devices
Here the devices accept voice commands as primary input and do come with integrated screen display which allows users to interact seamless in both touch and voice depending on the users comfort. This is much simpler, efficient and reduces cognitive load from user while perceiving and interacting. These are example of multimodal interaction that gives freedom and control to users.
Most of the devices are multimodal friendly but it’s up to you to decide if your user want multimodal interaction or Graphical user interface or Voice user interface as all these comes with its own pros and cons.
MMI Ecosystem
The diagram below shows the architecture of a MMI ecosystem which shows the communications between a smart house, car and interacting devices used by user namely smartphone, wearables through web and cloud.
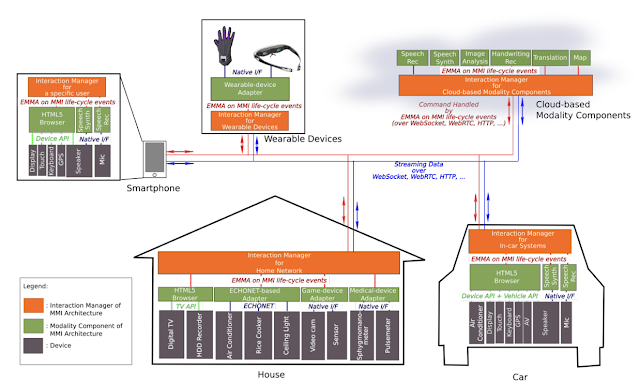
Image courtesy of W3.org
The MMI Architecture, along with EMMA (Extensible Multi-Modal Annotations), provides a layer that virtualizes user interaction on top of generic Internet protocols such as WebSockets and HTTP, or on top of more specific protocols such as ECHONET. The below diagram shows the communication layer between the user, multimodal interface, device, application and the integrating technology.

Image courtesy of W3.org
Where is multimodal Interaction used?
To start with “where is multimodal interaction used?”, The answer is everywhere but it just depends on the user if he wishes to use it or not and the application which the user is interacting. Most of the general applications on smart phones are MMI as google maps, chrome browsers, inbuilt application on smart phones. Most of daily used gadgets are capable of handling multimodal interaction be it Desktops, laptops, smart TV, thermostats, IOT devices and the list goes on. Manufacturing, Heath domain, Automobiles, Hi-tech Construction, IT enterprise solutions, Embedded digital devices are the places for MMI.

Strategy for use MMI
Diverse abilities. MMI provides users to use the most efficient mode of interaction among those proposed by the system depending on the constitutional position of the user.
Personalization. One input mode fits all context is not always true, with MMI the interaction could be customized for given task in an application as preferred by user.
Interaction patterns. Different users interact with application differently and designers should be aware for whom they are designing knowing the wide range of users.
Independence. Multimodal interfaces should empower older users to independently interact with the technology, even when there is a specific impairment (for example hearing loss or reduced sight).
Technology reliability. Users should be able to rely on the multimodal technology, especially in the case of assistive technology. For this reason, multimodal processing should be accurate and robust.
Privacy & Context of use. Users have privacy & various concerns in public spaces when using gesture & voice command, voice commands in noisy environment, inter use of speech, gesture, tactile when interacting and visual over audio depending on the context.
Oviatt’s ‘‘Ten Myths of Multimodal Interaction’’ (Oviatt, 1999) offers useful insights for those researching and building multi- modal systems, with a few especially apropos:
• Myth: If you build a multimodal system, users will interact multimodally. Rather, users tend to intermix unimodal and multimodal interactions. Fortunately, multimodal interactions are often predictable based on the type of action being performed.
• Myth: Multimodal input involves simultaneous signals. Multi- modal signals often do not co-occur temporally, and much of multimodal interaction involved the sequential (rather than simultaneous) use of modalities.
• Myth: Multimodal integration involves redundancy of content between modes. Complementarity of content may be more significant in multimodal systems than redundancy.
• Myth: Enhanced efficiency is the main advantage of multimodal systems. Multimodal systems may increase efficiency, but not always. Their main advantages may be found in other aspects, such as decreased errors, increased flexibility, or increased user satisfaction.
• Myth: Individual error-prone recognition technologies combine multimodally to produce even greater unreliability. In an approprivately flexible multimodal interface, people determine how to use the available input modes most effectively; mutual disambiguation of signals may contribute to a higher level of robustness.
Reeves et al. (2004) defined the following guidelines for multi- modal user interface design:
• Multimodal systems should be designed for the broadest range of users and contexts of use. Designers should support the best modality or combination of modalities anticipated in changing environments (for example, private office vs. driving a car).

• Designers should take care to address privacy and security issues in multimodal systems. For example, non-speech alternatives should be available in a public context to prevent others from overhearing provide information or conversations.
• Maximize human cognitive and physical abilities, based on an understanding of users’ human information processing abilities and limitations.
• Modalities should be integrated in a manner compatible with user preferences, context, and system functionality. For example, match the output to acceptable user input style, such as constrained grammar or unconstrained natural language.
• Multimodal interfaces should adapt to the needs and abilities of different users, as well as different contexts of use. Individual differences (for example, age, preferences, skill, sensory or motor impairment) can be captured in a user profile and used to determine interface settings.
• Be consistent – in system output, presentation and prompts, enabling shortcuts, state switching, etc.
• Provide good error prevention and error handling; make functionality clear and easily discoverable.

Limitations in multimodal interaction
Everything comes with limitation and trade-offs so is multimodal interaction the limitation could be unknown context of user, insufficient testing, technology constraints, processing information, integration, slip, delay, consistency, scalability.
Complexity vs Simplicity. Providing user with all possible interaction’s might increase the complexity in term of designing solution as you have many right option to consider while designing.
Personalization vs Customization. Multimodal interaction can be tailored to the specific preferences or needs of the user. This process might end up in an over- personalization of the interaction, making it difficult to the user to discover or experiment with alternative interaction modalities.
Independency vs Assistance. The cognitive effort required by different users varies and needs personalization depending on the user type, users with impairment and older users have different needs.
Ambiguity: Ambiguity arise when more than one interpretation of input is possible. This happens normally when a gesture, speech command or touch input overlaps with each other or when one modality has more than one interpretation and this could be intended or un-intended in the environment.
Ambiguity can be solved by three methods namely:
Prevention. Imposes users to follow predefined interaction behaviour according to the required input to allow change in the state.
A-posterior resolution. This method uses a mediation approach where the users are allowed to confirm, repeat, delayed reaction, undo & repair.
Approximation resolution. Here ambiguity is removed by using a fuzzy logic, Markov random field, Bayesian network system and eliminate the ambiguity.
Conclusion
The above content gives an understanding about how multimodal interaction can help users in competing given task effectively. MMI help in making interaction simple, fast and efficient providing users more freedom and control to interact with different applications, devices & technology. Designers needed to determine the most intuitive and effective combinations of input and output modalities for different users, applications and usage contexts, as well as how and when to best integrate those modalities.
About Author
Balaji C P

References
https://www.webdesignerdepot.com/2018/11/5-trends-of-voice-ui-design/ https://www.w3.org/TR/mmi-arch/
https://www.w3.org/TR/emma/
https://www.w3.org/2013/10/mmi-charter
https://www.w3.org/2002/mmi/
https://medium.muz.li/voice-user-interfaces-vui-the-ultimate-designers-guide8756cb2578a1
https://www.highervisibility.com/blog/how-popular-is-voice-search/ https://www.greenwoodcampbell.com/blog/archive/how-we-integrated-google-assistantvoice-interface-with-a-website/
https://build.amazonalexadev.com/What_is_voice_user_interface_VUI.html https://disqus.com/by/josephjaquinta/
https://www.bbc.com/news/technology-38539326 http://ceur-ws.org/Vol-2101/paper3.pdf https://voicify.com/understanding-multimodal-interactions/ https://developers.google.com/assistant/conversational/overview https://www.radiantvisionsystems.com/blog/wave-your-hand-3d-gesture-recognitionsystems http://jmlr.org/papers/volume17/14-468/14-468.pdf http://www.dhs-ltd.com/toyota-a-long-collaboration/
https://sites.google.com/view/multimodalvis https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1071581913001407

Sunday, 22 January 2017
A Beginner's Look At Prototype Design Tool - Mockplus v2.3
About Author
Berry Sarah
Email: berry@jongde.com Enthusiast for developing #prototypingtools, hoping to make friends with all like-minded guys. #ux #design #prototyping.


















%20in%20India.png)

